
In today’s interconnected world, we rely heavily on cables to transmit electrical signals, data, and information. Whether it is powering devices, connecting networks, or transferring data between devices, cables play a crucial role in our everyday lives.
However, when delving into the world of cables, it is essential to understand that not all cables are the same. They come in various types, each designed for specific purposes and applications.
What are cables?
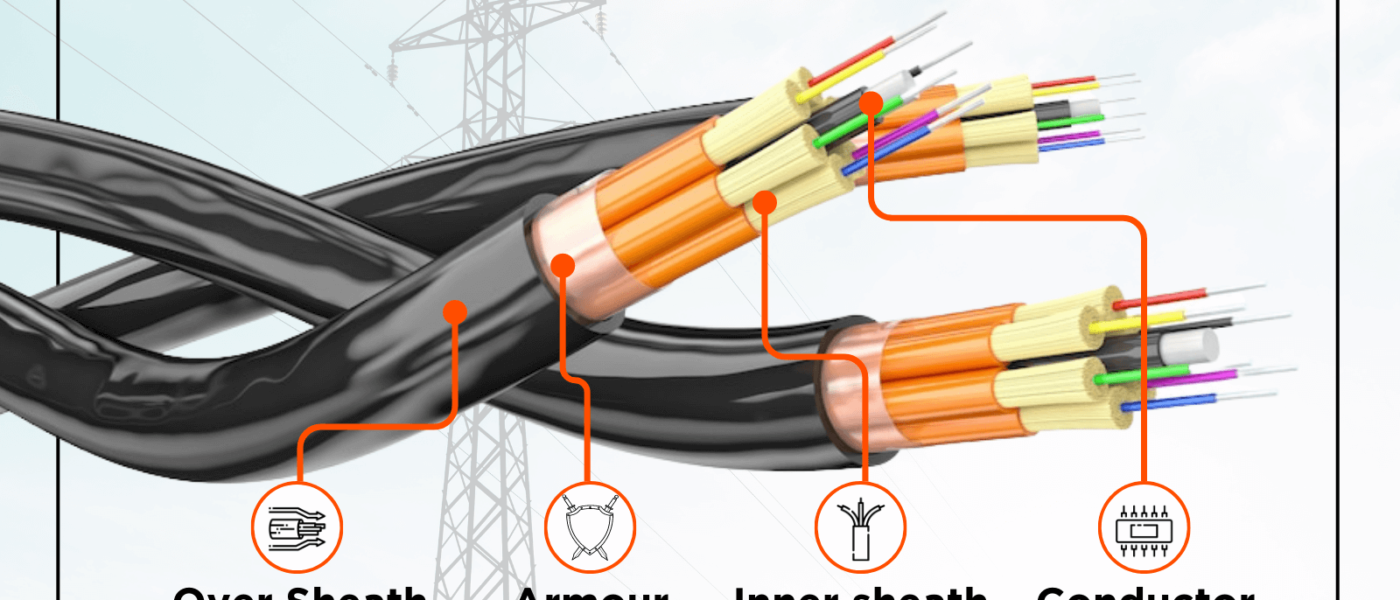
Cables are structured assemblies of one or more wires enclosed within a protective covering. They transmit power, signals, or data from one point to another. Power cables consist of three primary components. They include:
- Conductor: It serves as the conducting path for current within the cable.
- Insulation/dielectric: It withstands the service voltage and isolates the live conductor from other objects.
- Sheath: It acts as a protective layer, preventing moisture from entering the cable and safeguarding it against external influences such as chemical or electrochemical attacks and fire.

What are the different types of cables & where are they used?
There are various types of cables, each carefully engineered to meet diverse applications’ requirements and challenges. A few common types and use of cables are:
- Coaxial cable
Coaxial cable consists of an inner conductor surrounded by a concentric conducting shield. They are used for transmitting television signals. Additionally, coaxial cables are used by telecommunication companies and internet service providers to transmit data, video, and voice to residential areas.
2. Fibre-optic cable
They contain one or more optical fibres that carry light. Due to their high bandwidth, they are used for long-distance and high-performance data networking.
3. Ethernet cable
Ethernet cables are also known as network cables. They connect devices to local area networks (LANs) and the internet. They establish connections between modems, routers, computers, and other wired Internet-capable devices, enabling broadband signal transmission. They are commonly used in homes and offices.

4. HDMI cable
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) cables are used for transmitting audio and video signals between devices, primarily for connecting entertainment devices like TVs, DVD players, gaming consoles, and audio/video receivers.
5. Ribbon cable
Ribbon cables consist of multiple conducting wires running parallel and attached to each other. They are used inside hard drives, CD drives, floppy drives, etc.
6. USB cable
Universal Serial Bus (USB) cables are widely used for connecting various devices to computers and other hosts. USB cables transfer data, provide power, and support other functionalities. They are used for connecting smartphones, external hard drives, printers, keyboards, mice, and many other peripherals.
7. Power cable
Power cables are designed for transmitting electrical power from a power source to electrical devices or equipment.
What is the difference between cables and wires?
Cables are often confused with wires, as both terms are used interchangeably. However, it is important to recognise that cables and wires have distinct characteristics and serve different functions within electrical and electronic systems. Here are some differences between cables and wires:
| Wires | Cables | |
| Definition | Single strand or group of strands of conductive material | Multiple insulated wires grouped together, often with additional protective layers |
| Composition | Single conductor | Two or more conductors |
| Purpose | Primarily used for carrying electrical current | Used for transmitting data, power, or signals |
| Size | Smaller in diameter and thinner | Can have a larger diameter due to the presence of multiple conductors and protective layers |
| Application | Commonly used for internal connections | Used for longer-distance transmissions, networking, power distribution, connections |
5 things to consider before buying cables
When purchasing cables, there are several important factors to consider. Here are five key things to keep in mind:
- Cable type and compatibility
- Cable length
- Quality and durability
- Bandwidth and speed requirements
- Current capacity
In conclusion, cables are vital components in electrical and communication systems. Understanding the different types of cables allows for informed decision-making when selecting the appropriate solution for a wide range of industries and applications. By utilising the appropriate cable, reliable and efficient connectivity can be achieved.
